Some important factors from "Concepts of Programming Languages (global edition) 11ed. - Robert W. Sebesta"
:Chapter 6
⬥FORTRAN: array & COBOL: record
⬥primitive data types(4): integer, float, boolean, character
⬥string operations: assignment, catenation, substring reference, comparison, pattern matching.
⬥3 approaches to supporting the dynamic allocation and deallocation for dynamic length strings
-linked list
-store strings as arrays of pointers to individual characters allocated in the heap
-store complete strings in adjacent storage
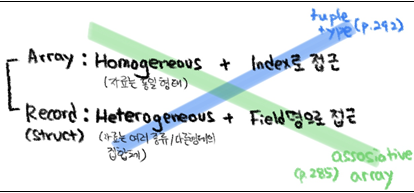
⬥2 types of structures(array, record) & tuple type/associative arrays
⬥purpose of pointers: indirect addressing, dynamic storage(dynamic variables in heap)
⬥garbage(p.302): an allocated heap-dynamic variable that is no longer accessible to the user program
⬥memory leakage: The first heap-dynamic variable is now inaccessible, or lost
⬥dangling pointer: a pointer that contains the address of a heap-dynamic variable that has been deallocated.
⬥eager approach(if count=0, retrieve immediately) VS lazy approach(if count=0, leave it and retreive later if short on memory)
⬥Casting(explicit type conversion) VS Coercion(implicit/automatic type conversion)
⬥strongly typed(make it compatible through casting=Java, C#) VS weakly typed(coersion=C)
⬥name type equivalance(stronger) VS structure type equivalence
⬥A data type defines a set of values and a collection of operations on those values. A type system is a set of types and the rules that govern their use in programs. Every typed programming language defines a type system.(p.317)